When compared with traditional methods, estimation in Agile is difficult since the requirements are mostly coarse-grained. Also, the lack of upfront planning makes it difficult to estimate accurately. Fortunately, over a period of time, Agile teams have identified techniques that have helped them estimate what they have and proceed with the work. In this article, we will go through the top 3 Agile Estimation techniques that are used widely.

#1. Planning Poker
Planning Poker is a consensus-based estimation technique, which is done by the team together. This meeting typically includes the primary stakeholders like the Development team, the SCRUM master, and the Product Owner. Other stakeholders can be included based on necessity. Every estimator in the team holds a deck of Planning Poker cards. These cards have values 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, and 100 representing story points.
The Product Owner starts reading out each user story one by one. At the end of every user story, the team gets any functional questions clarified with the Product Owner. After that, the SCRUM master starts the timer for the team to estimate. Every team member analyses and privately selects an estimate from his deck of cards. But they keep the estimate to themselves as of now. The SCRUM master waits for everyone to confirm that they have completed their estimation. In some cases, he may put a countdown timer for the team to finish their estimation.
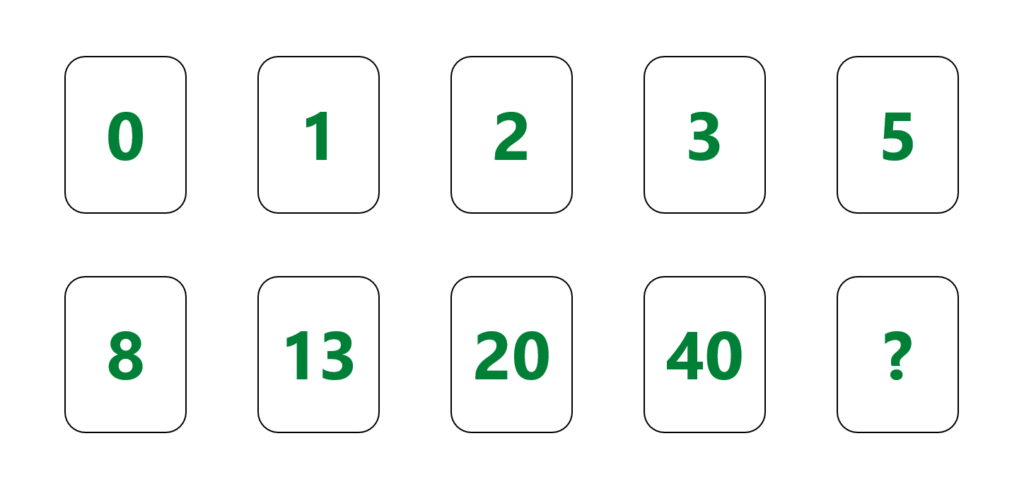
Once all are done with their estimation, the SCRUM master asks everyone to reveal their estimate (card). After which, the estimates of everyone are compared. If the estimates match with everyone, then there is no discussion, and that “number” is considered the final estimate. But if the estimates do not match (which is quite often the case), then the team members with estimate variance explain why they think their estimate is HIGH or LOW. After discussion, this process is repeated until consensus is achieved.
One major advantage of this approach is that this takes into consideration the opinion of all disciplines involved in the team. And moreover, since the estimates are selected privately, there is no bias in individual opinion. This brings out any genuine risk involved in the user story in context.
Video: Top 3 Agile Estimation Techniques
#2. T-Shirt Sizing
T-Shirt sizing estimation is done at a much earlier stage in Agile Project. Typically after receiving the Product roadmap for the year from Product Management. This technique is used get an idea of how much “long” does a feature take to be delivered. It also helps the team in understanding the resource needs based on what the roadmap is asking. When compared with estimation in Sprint Planning/Backlog grooming, T-Shirt sizing is more useful when the requirements are in much earlier stage. And when there is too much ambiguity and uncertainty to estimate using specific story points.
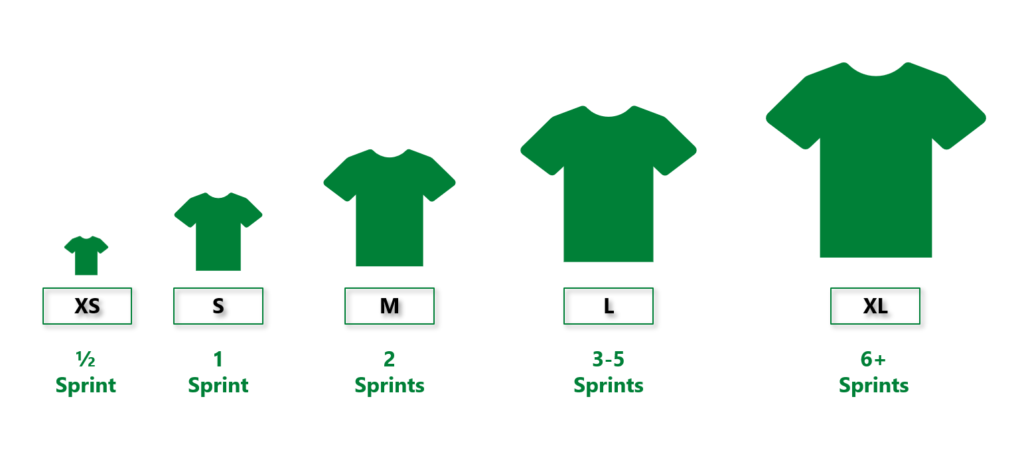

In many cases, each T-Shirt size is mapped to Sprint duration (refer above diagram). This technique is preferably applied to Epics or features. It is a useful tool for Engineering Managers, SCRUM masters or Product Managers to size and look at the milestones of the Project. Now looking at the list of features and their interdependencies, the T-Shirt sizes would give a holistic picture of the whole timeline that we are dealing with. This helps managers to deal with any new resource requirements if required.
One advantage with this technique is that it is fast. Team need not think about low level tasks and analyse to estimate. In a way this is Top-Bottom estimation. It is these T-Shirt sized features which get decomposed into user stories, which are in turn estimated with comparatively more definitive “story points”.
Note: There are teams that map story points to T-Shirt sizes, instead of sprint durations. Whatever works for them
#3. Affinity Mapping
Third among top 3 agile estimation techniques, Affinity Estimation is a technique used by Agile teams in situation where user stories need to be estimated quickly and easily. The estimation is done in story points. This method is of great advantage when the backlog is not estimated and the team needs to estimate them quickly. This is useful when the team is small and the project has just started.
First step is to create a scale on wall ascending in size from left to right. Many teams use T-Shirt sizes for this (refer diagram below). And then the Product Owner provides the list of user stories to the team. Each team member individually estimates on their stories (without discussion). They place the story (sticky note) on the estimate bucket they feel it falls under.
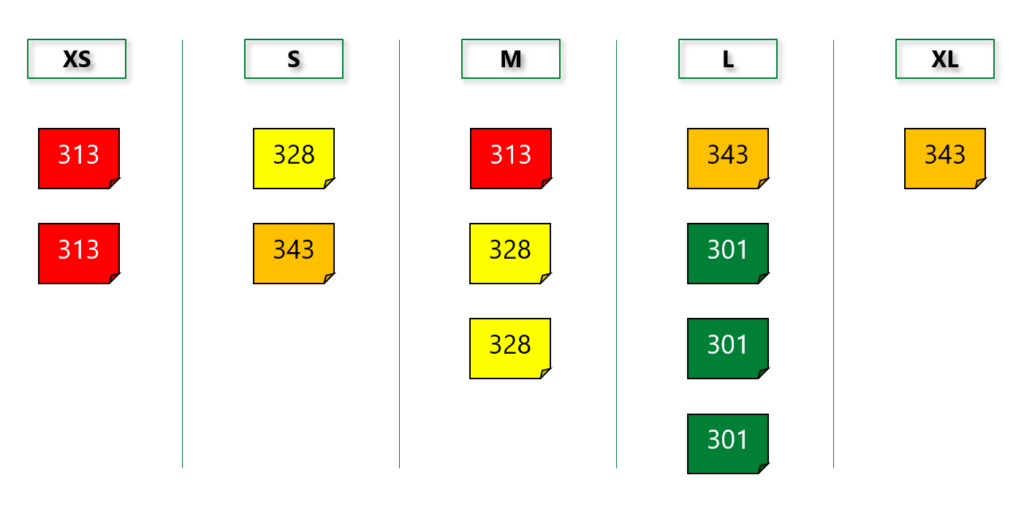
After the stories are placed under the estimate bucket by the team, they start discussing on the variance of estimates. They discuss the technical and functional reasons on why they have arrived at the estimate. The Product Owner is available to clarify on any functional queries. Once clarified, the team calibrates the wall and start editing the estimate and place stories under the estimate bucket they feel is relevant. This exercise may be repeated until the estimates are calibrated.
Conclusion
Although there is no silver bullet for comprehensive estimation in Agile, these techniques can suffice. Given the adaptive nature of requirements in Agile, simple estimation techniques are more reliable than complex bottom-up techniques. Moreover, complex techniques has cost associated with it and drains away a lot of team energy whenever the requirements change. These top 3 agile estimation techniques should be helpful.
Choose one of these techniques depending upon the level of planning you are in the agile Project. And a strong suggestion here is to map the actuals with estimates after the Project so that you can benchmark some numbers.

Our PMI® PMP®-Prep Course
If interested in this course, click here
- Case study based training
- LIVE instruction 36 Hours
- Post course guidance
- Exercise per topic
- 4 Mock exams for practice
- WhatsApp group support

Our PMI® ACP®-Prep Course
If interested in this course, click here
- WhatsApp group support
- 4 Mock exams for practice
- Exercise per topic
- LIVE instruction 20 Hours
- Post course guidance
- Case study based training

JD (Coach/Instructor/Writer)
JD (a.k.a Janakiram) is a Project Management Coach, Trainer Author and Practitioner @Zaidan Consulting. He comes with around 17+ Years of experience primarily from the Software Industry. He is certified on PMI® PMP®, ACP®, Scrum Alliance CSM and Microsoft Certified Solution Developer on C#.NET. He has also authored the book “Practical Agile for Beginners”

About Zaidan Consulting
Zaidan Consulting are specialists in Project and Program Management space. Our training offerings include:
- Project Management Training
- Agile Training
- PMI®-ACP® Prep Training
- PMI®-PMP® Prep Training
- PMI®-CAPM® Prep Training
- ScrumStudy™ Authorized Training Partner (A.T.P)
Or you can contact us @+(91) 7672011471
Or Email us: contact@zaidanconsulting.com

Good one